Introduction
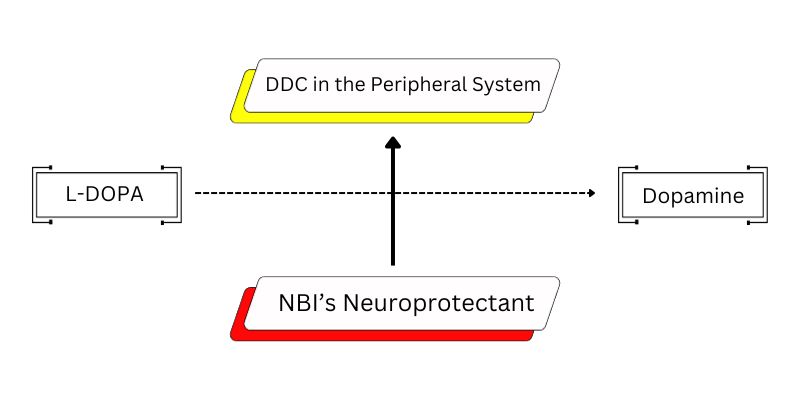
The pathology of Parkinson’s is the degeneration of cells in the mid brain that otherwise regulate the release of dopamine. The body is thus supplemented with L-DOPA, the precursor of dopamine, which also has the potential to cross the blood brain barrier. However, innate DOPA decarboxylase converts the L-DOPA into dopamine while in the peripheral system.
The body thus remains dopamine deficient since the molecule by itself cannot cross the blood brain barrier. It is observed that the role of enzymes such as DOPA decarboxylase is critical to ensure L-DOPA is not converted to dopamine in the peripheral system. Molecules that can inhibit DOPA carboxylase are thus essential to manage Parkinson’s. NBI in collaboration with CSIR-IITR used advanced molecular docking techniques to predict the activity of over 10,000 molecules derived from natural sources. In addition to predictive active receptor binding data, the molecular docking technique was also used to predict the ability of the molecules to cross the blood brain barrier. With this systematic approach, an approximate 10 compounds were short listed to take forward to the next level of screening and identification of the ideal formulation.
In vitro screening of DDC inhibition potential: The shortlisted molecules from in silico screening were primarily subjected to in vitro cytotoxicity testing at NIPER. The screening was carried out on multiple cell lines. Based on the non-toxic nature of 3 active compounds even at high concentrations, they were selected to estimate their DDC inhibition potential. A dose response curve was observed with increasing concentrations of the active molecules on the enzyme. A 100% inhibition was observed with doses as low as 1200 – 1300 µg/ml. The number of molecules after completion of the in vitro assay was shortlisted to 3. The next stage of evaluating the compound was through its efficacy in human subjects.
Dr Parthasarathi Ramakrishnan
Dr Ramakrishnan serves as Principal Scientist of CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow at Computational Toxicology Facility, Toxicoinformatics Research and leading BIRAC-BioNEST supported Centre for Innovation and Translational Research (CITAR), and Environmental Monitoring and Intervention Hub (DSIR-CRTDH-IITR).
Dr Partha earned his PhD from CLRI, University of Madras and he served as a scientist with highly reputed institutions like the Lawrence Berkeley National Labs, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Sandia National Laboratories, USA. He has more than 20 years of research experience in applied biochemistry to unravel important issues in human health and the environment. His lab is currently involved in the development of AI & Machine Learning based computational toxicity models, biomolecular simulations, databases, and developing innovative predictive approaches relevant to translational research.
Dr. Aashish Gambhir
Dr Aashish Gambhir is a dynamic physician obtaining his graduate degree in medicine from the prestigious MAMC medical College in Delhi. He specialised in super speciality subjects pertaining to modern medicine with significant clinical exposure. Later he obtained Diploma in Radiation Medicine (DRM), a post graduate qualification in the rapidly advancing field of nuclear medicine from the defence research institution (DRDO– INMAS). During this period, he obtained accolades, such as the gold medal for his paper on parathyroid Imaging. He developed this further at leading national institutions such as the Apollo hospitals, Chennai, where he received extensive clinical training in gamma camera/SPECT Imaging, PET imaging and nuclear Theragnostic while working with multiple radio tracers for and Investigative and therapeutic purposes. Dr Gambhir is certified by the Atomic Energy Review Board. (AERB). Over the last 12 years he has been operating as consultant and at various facilities in the country Including House of Diagnostics, Yashoda Hospitals, Narula Diagnostic and Ganesh Diagnostics which offer a full suite of nuclear medicines studies for patients.
He has been actively involved in pharmaco-scintigraphy work and remains an active member of the society for nuclear medicine in India. He has an active understanding of plant based long chain molecules, which often promise a reduction of side-effects (as opposed to chemically synthesised drugs). At NBI Biosciences he has led and been closely associated with experiments using Scintigraphy Showing the efficacy of certain plant derived molecules replacing carbidopa with greater efficacy in Parkinson’s disease. He has also Investigated the delivery technology (SLIDD) to the human colon. Both of these have been patented by NBI Biosciences.
Dr. Kamireddy Kiran
Dr Kamireddy worked as Research Scientist at NBI Biosciences and was involved in R&D activities that relates to extraction and purification of plant actives at CSIR-CFTRI, NBI collaborator.
Dr. Kiran has 5-Years of lab experience and holds a PhD in the field of Biotechnology and extensively worked in the field of botanical cultivation and testing., Kiran works on the focus of plant extracts, isolation, and purification of bioactive compounds. Presently he is working as a social innovator in BIRAC sponsored project.